Cell Cycle Pmat Mitosis | During the growth phase of the cell cycle, the genetic material of the cell (chromosomes) is doubled. During this time, the cell completes a number of stages. Two parallel signalling pathways, atm and atr respond to genotoxic stress by activating their downstream target proteins including the two. Any specialized cell — muscle cells and nerve cells, for example — leave the cell cycle and enter into what's called g0. These initially remain attached to each other with each strand called a chromatid.
During mitosis , the cell's nucleus divides. The biology project > cell biology > intro. Although cell growth (in terms of cytoplasmic increase) is a continuous process, dna synthesis occurs only during one specific stage in the cell cycle. The first stages of the cell cycle involve cell growth, then synthesis of dna. Mitosis is nuclear division plus cytokinesis, and produces two identical daughter cells during prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.

All of the cell's energy is focused on the complex and orderly division into two similar daughter cells. Mitosis is a stage in the cell cycle when the nucleus divides. To cell cycle & mitosis > tutorial. The cell cycle describes the cyclic sequence of events in eukaryotic, proliferating cells. Finally, note that the m phase of the cell cycle can also be subdivided. Cells regulate their cell cycle in two distinct ways: Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. Cornell whitefish mitosis cell division: In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane. The division of the cell in two (cytokinesis) occurs concurrently with. Any specialized cell — muscle cells and nerve cells, for example — leave the cell cycle and enter into what's called g0. Cell cycle regulation and cancer. Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle process by which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus.
Any specialized cell — muscle cells and nerve cells, for example — leave the cell cycle and enter into what's called g0. Maintains the correct chromosome number to make a new daughter cell 7. What are the stages of the cell cycle? Cells regulate their cell cycle in two distinct ways: Cells in g 0 no longer divide.
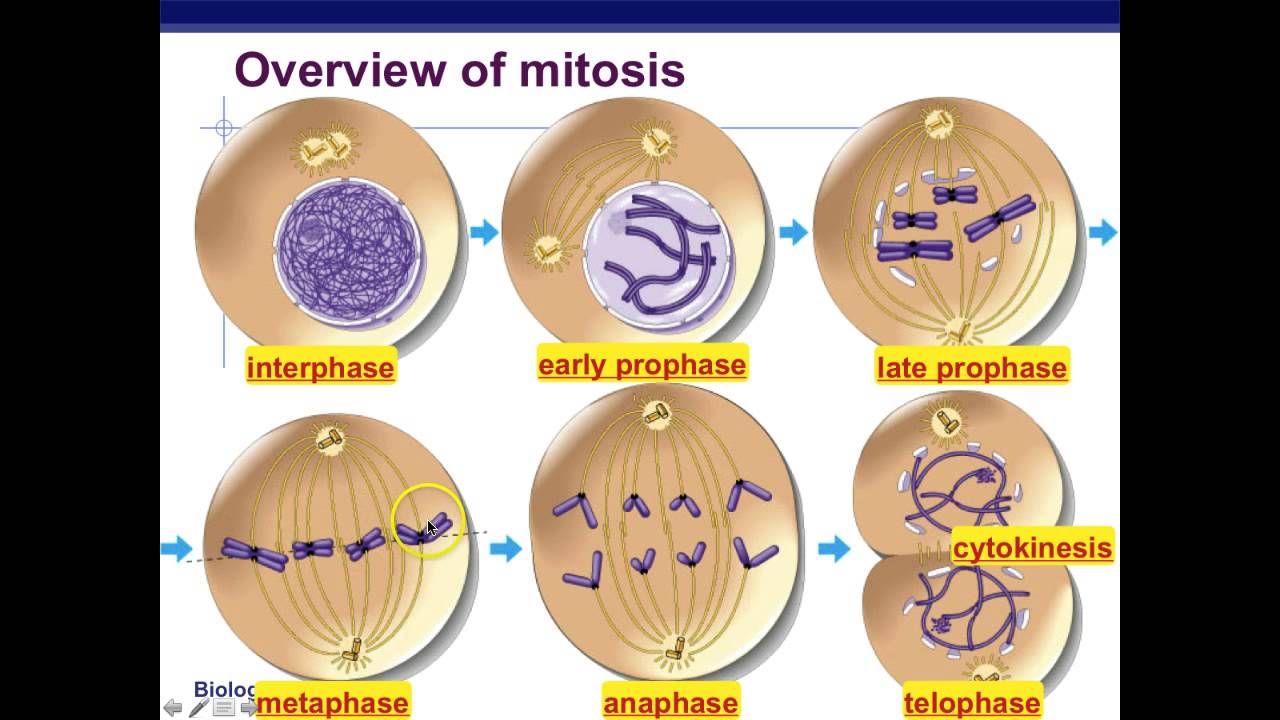
Both diploid and haploid cells can undergo mitosis. These events include the duplication of its dna (dna replication) and some of its organelles. Strands of chromosomes begin to condense and become visible b. The g1 phase is a growth phase during which proteins and cellular constituents required for mitosis such as microtubules are created. Mitotic cell cycle consists of long interphase(which is sub divided into g1, s and g2 phases), a short m stage (or mitotic stage, subdivided into prophase. During this time, the cell completes a number of stages. Start studying cell cycle & mitosis. What is the cell doing during interphase. In mitosis and cytokinesis, the contents of the dividing cell are equally distributed between two daughter cells. Mitosis is preceded by interphase and is divided into four distinct stages: The first stages of the cell cycle involve cell growth, then synthesis of dna. During interphase, the cell spends most of its time performing the functions. Interphase (in between divisions phase grouping g1 phase.
Start studying cell cycle & mitosis. This makes a lot of sense, because mitosis is essentially like making a photocopy: In mitosis and cytokinesis, the contents of the dividing cell are equally distributed between two daughter cells. It is represented by dna duplication followed by nuclear division (karyokinesis) which in turn is followed by cytokinesis. At several points in the mitotic cell cycle, a checkpoint operates.
Two copies of each chromosome are produced; During mitosis , the cell's nucleus divides. Cornell whitefish mitosis cell division: Interphase (in between divisions phase grouping g1 phase. Mitotic cell cycle consists of long interphase(which is sub divided into g1, s and g2 phases), a short m stage (or mitotic stage, subdivided into prophase. Confused about mitotic cell division? Checks/ regulators for each step to ensure timely progression g1 phase, time in this stage can vary in length in species. During g1, when the conditions are favorable, certain proteins likewise, if the cell is not healthy or large enough, or the environmental conditions are not favorable, the cell cycle stops here to prevent cell injury. Cell growth and protein production stop at this stage in the cell cycle. These initially remain attached to each other with each strand called a chromatid. The cell cycle is made up of two main stages: To cell cycle & mitosis > tutorial. The cell cycle is a continuous process, but to make it easier to study it can be broken down into four phases.
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle process by which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus pmat mitosis. What are the phases of mitosis?
Cell Cycle Pmat Mitosis: These events can be divided in two main parts:
comment 0 Post a Comment
more_vert